
Foreword
Organic acids can react with alcohols to produce esters. The carboxyl group is the functional group of the carboxylic acid. Except for the formic acid (H-COOH), the carboxylic acid can be regarded as a derivative after the hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon molecule are replaced by the carboxyl group. It can be expressed by the general formula (Ar) R-COOH. Carboxylic acids are often widespread in nature in the free state or in the form of salts and esters. Some of these compounds are involved in the life process of animal and plant metabolism. Some are intermediates of metabolism, some have significant biological activity, which can prevent and cure diseases, and some are organic synthesis, industrial and agricultural production and pharmaceutical industry raw materials.
How to detect the common organic acids found in fruits?
The common organic acids in fruit are citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, acetic acid, succinic acid and oxalic acid, etc., are the main flavor nutrients in the fruit, can soften blood vessels, promote the absorption of calcium and iron, can stimulate the secretion of digestive glands, have the function of increasing appetite, help digestion and absorption and quench thirst and relieve heat.

So how do you detect the organic acids that are common in fruits? This has become a concern of more people.
We have previously shared how to use INNOTEG LC columns to efficiently complete the determination and control of synthetic colorants in food(Click here to read). In this article, INNOTEG will continue to bring you the detection of organic acids in fruits.
Application scheme for detecting organic acids in fruits
No.1
Standard concentration:
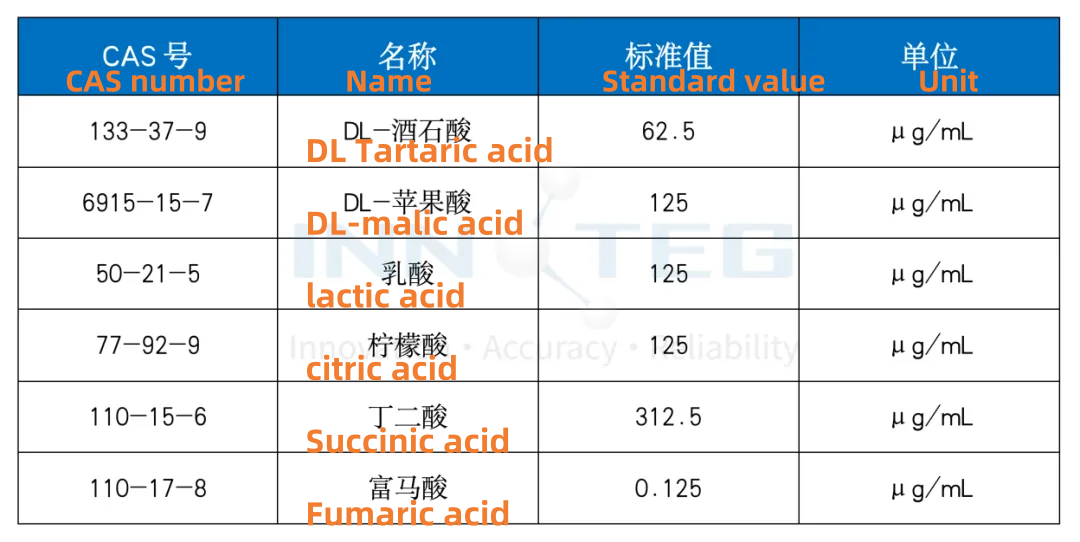
Six organic acid mixed standards were used for testing:
No.2
Chromatographic Condition
Innode column: YND-P-C18 5um 4.6 * 250mm;
Sample intake: 20 μ L;
Column temperature: 40℃;
Mobile phase: elute with 0.1% phosphate acid solution-methanol =975 X 2.5 (volume ratio) for 10 min, then make the methanol phase to 100% and equilibrate for 5 min, and then adjust the mobile phase to the ratio of 0.1% phosphate acid solution-methanol = 97.5+2.5 (volume ratio), equilibrate for 5 min;
Detection wavelength: 210nm
No.3
Test spectra
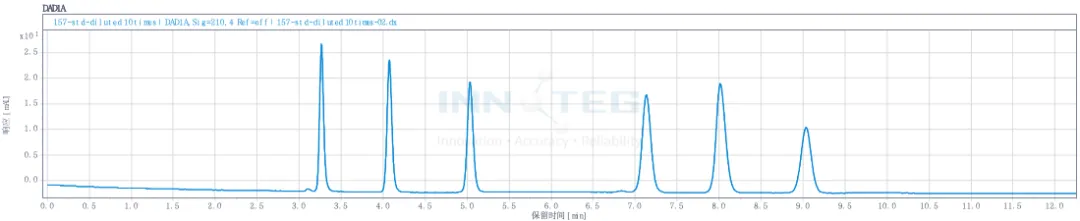
Determine the reference GB 5009.157-2016 chromatography conditions for detection, six common organic acids can be well separated, to meet the requirements of national standards.
No.4
Advantage and characteristics of YND-P-C18
Compared with conventional C18, the Incent INNOTEG YND-P-C18 column increases the retention of no or weak hydrophilic or polar samples on other columns, so that no C18 functional group collapse in high proportion or pure aqueous phase!
● Suitable for the separation of hydrophilic samples;
● Strong retention under the condition of the mobile phase containing a high proportion of water;
● Has a longer chromatcolumn lifetime in the drainage mobile phase.

Product information
517-54625 INNOTEG YND-P-C18,5um 4.6*250mm LC Column
517-54615 INNOTEG YND-P-C18,5um 4.6*150mm LC Column
For inquiry, please email: [email protected]

2 Comment(s)
1
1
1
1
1
Leave a Comment